THE FOUR C's:
Cut
Cut is a very important quality factor, and probably the most challenging, of the four Cs to understand. The brilliance of a diamond depends heavily on its cut, which give a diamond that brightness that seems to come from the very heart of the diamond. The quality of the cut is a result of just the right angles, proportions and finish of the diamond. It is the quality of the cut that gives a diamond its ability to handle light, which in turn leads to its dazzling brilliance and fire.
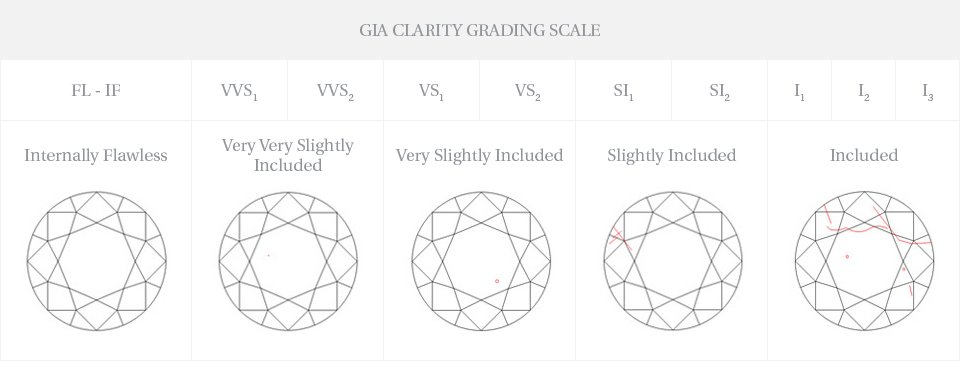
Clarity
Almost all diamonds contain some inner flaws, or inclusions, that occur during the formation process. These inclusions are the ‘birthmarks’ of the diamond. The visibility, number and size of these inclusions determine what is called the
clarity of a diamond. The inclusions interfere with the path of light through the diamond and therefore, diamonds that contain a lower degree of these inclusions create more brilliance. The better the clarity of the diamond the more expensive the diamond will be. Most inclusions in a diamond are so small that it is not possible to see them with the naked eye.
Color
A diamond is graded based on its lack of colour. The
less colour, or the
more colourless a diamond is, the greater its value and its visual appeal. Diamond colour grades range as follows:

- D-F (Colourless) – These are the rarest and highest colour grade diamonds
- G-J (Near Colourless) – These are rare diamonds still with a bright white colour
- K-M (Faint) – These are not so rare diamonds with a slight yellow tint
- N-R (Very Light) – These are widely available diamonds with noticeable yellow tint
- S-Z (Light) – These grade of diamonds are plentiful in the market and therefore the lowest colour grade
Colourless and Near Colourless diamonds are the most desirable since they allow the most refraction of light (sparkle).
Carat (weight)
Diamond Carat is the unit of weight by which a diamond is measured As diamond carat weight increases so does its value, however it is important to note that as larger diamonds are rarer than smaller ones, the value of a single diamond increases exponentially with its carat weight. Often the carat weight of a diamond is used when talking about the diamonds size. Although this is not strictly correct, naturally, as the weight of a diamond increases, so does its size, and for this reason people use Carat weight as an indication of size.
The table below shows the approximate diameter of a round and princess cut diamond as the carat weight changes:
| Diamond Weight in carats: |
Round Diamond diameter in mm: |
Princess Diamond size in mm: |
| 0.10ct |
3.00mm |
2.50mm |
| 0.20ct |
3.80mm |
|
| 0.25ct |
|
3.50mm |
| 0.30ct |
4.30mm |
|
| 0.40ct |
4.80mm |
|
| 0.50ct |
5.20mm |
4.40mm |
| 0.70ct |
5.85mm |
|
| 0.75ct |
|
5.00mm |
| 0.90ct |
6.30mm |
|
| 1.00ct |
6.50mm |
5.50mm |




Sign In
Create New Account